Why Mexico Is the Top Alternative to China for Manufacturing | 2025 Nearshoring Trends
U.S. manufacturers and investors are increasingly looking south of the border for their next growth opportunity. Mexico overtook China to become the United States’ largest trading partner, a significant shift fueled by supply chain realignments, rising geopolitical tensions, and the growing appeal of nearshoring strategies. This trend is especially pronounced in automotive and electronics industries, where Mexico offers a compelling mix of lower costs, proximity, and trade advantages that have made it a more competitive option than China.
Below, we break down the key reasons – why investing in Mexico has become more attractive than investing in China for the U.S. focused manufacturing.
Mexico’s Nearshoring Surge vs. China’s Slowdown
More companies are rethinking their manufacturing strategies and shifting production to nearby regions to gain better control, reduce lead times, and increase supply chain resilience. Mexico now sends more goods to the U.S. than China, a big change from a few years ago. Trade tensions and pandemic-related delays have pushed businesses to work with nearby, trusted countries.
Investment is following the trend. Mexico is receiving billions in new factory projects, especially in the automotive and electronics sectors. Tesla’s new EV plant in Nuevo León and the arrival of Chinese suppliers highlight how Mexico is becoming a key hub for North American manufacturing.
Reasons Why It’s More Attractive to Invest in Mexico than in China
As global supply chains realign in response to rising costs, geopolitical shifts, and demand for resilience, Mexico has emerged as a top alternative to China for manufacturing investment. Here are the key factors driving Mexico’s rise as a preferred manufacturing destination over China:
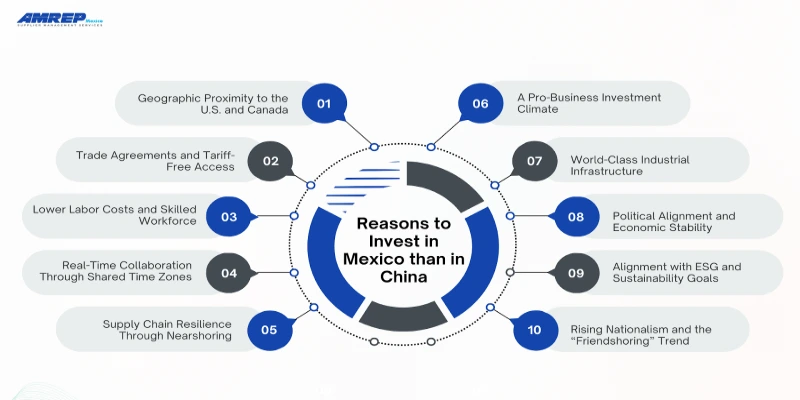
1. Geographic Proximity to the U.S. and Canada
Mexico’s most immediate advantage is its location next door to the U.S., the world’s largest consumer market. This translates into real, measurable benefits across the supply chain.
- Faster shipping times: Mexican goods reach the U.S. in 2–5 days by truck, compared to 15–30+ days by sea from China.
- Lower freight costs: Trucking a 53-ft trailer from Mexico can cost ~$2,500, vs. $5,000–$15,000 for a 40-ft container from China.
- Streamlined customs: Mexico’s well-established cross-border infrastructure (e.g., IMMEX, USMCA) reduces bureaucratic friction and delays.
For North American businesses, this proximity means faster time-to-market, better visibility, lower logistics costs, and fewer supply chain disruptions.
2. Trade Agreements and Tariff-Free Access
One of the strongest financial arguments for Mexico is the tariff advantage under USMCA, which China lacks.
- Zero tariffs: Under USMCA, most goods made in Mexico enter the U.S. duty-free.
- Punitive tariffs on China: U.S. tariffs on Chinese goods average 19.3%, with some sectors facing 25–100% duties.
- Global market access: Mexico holds 13 FTAs with 50 countries, opening access to both U.S. and EU markets. China’s FTAs don’t include the U.S.
Companies can eliminate millions in tariffs simply by shifting production from China to Mexico, gaining a major cost and compliance edge.
3. Lower Labor Costs and Skilled Workforce
Mexico now outcompetes China in both labor cost and talent readiness.
- Lower wages: Average manufacturing wages are ~$4.69/hour in Mexico, vs. $5.05/hour in China and fully loaded labor costs are still 20–30% lower.
- Youth advantage: One-third of Mexico’s population is under 19, offering a deep pipeline of workers.
- Technical skill: Mexico graduates more engineers per year than the U.S. and has a strong reputation for industrial craftsmanship.
- Labor stability: Reforms under USMCA have improved labor rights while maintaining Mexico’s competitive cost structure.
This balance of cost efficiency and growing skill makes Mexico ideal for advanced manufacturing, especially in automotive and electronics.
4. Real-Time Collaboration Through Shared Time Zones
Time is money, especially in modern supply chains.
- Same-day decisions: Mexico shares time zones with the U.S., enabling real-time communication without 12-hour lags.
- Youth advantage: Production issues or design tweaks can be handled instantly, not overnight.
- Easier oversight: U.S. executives can easily visit plants without long flights or language barriers.
For companies running agile or just-in-time models, Mexico provides seamless operational coordination.
5. Supply Chain Resilience Through Nearshoring
The global pandemic exposed the fragility of long-distance sourcing, and firms are adapting.
- Reduced shipping risk: Nearshoring to Mexico avoids container shortages, port delays, and maritime chokepoints.
- Greater control: Proximity allows for better oversight, faster adjustments, and more responsive logistics.
- Strategic shift: The “China Plus One” and “China Plus Nearshoring” strategies are gaining traction, and Mexico is the most logical alternative.
Nearshoring to Mexico is not just a cost-saving move; it’s a risk-mitigation strategy for long-term stability.
6. A Pro-Business Investment Climate
Mexico has actively cultivated an investor-friendly environment that encourages manufacturing expansion.
- Plug-and-play zones: Modern industrial parks come with utilities, security, and export support.
- Incentives: Tax benefits, simplified permitting, and workforce training programs.
- Public-private partnerships: Collaboration with local governments helps streamline logistics and reduce friction.
Compared to China’s tightening regulations, especially in tech, data, and finance, Mexico is increasingly the more predictable and accessible market.
7. World-Class Industrial Infrastructure
Mexico’s manufacturing base is not emerging; it’s established and thriving.
- Automotive: Over 4.2 million vehicles produced in 2024, now 5th in global output.
- Electronics: Over $100 billion in electronic exports annually.
- Cluster advantages: States like Jalisco, Baja California, and Nuevo León are packed with suppliers, logistics hubs, and talent pools.
- Industrial real estate boom: Demand for facilities has driven 30%+ growth since 2019, with vacancy rates under 3% in top zones.
With decades of U.S.-Mexico integration under NAFTA/USMCA, manufacturers can plug into a mature, North America-ready ecosystem.
8. Political Alignment and Economic Stability
While no market is without challenges, Mexico offers more policy certainty than China.
- Stable currency and interest in foreign direct investment.
- Consistent legal frameworks through USMCA, including mechanisms for resolving trade disputes.
- Low geopolitical tension with the U.S., unlike China, which faces export bans, sanctions, and decoupling concerns.
Investors value predictability and Mexico provides a lower-risk regulatory and political climate for long-term planning.
9. Alignment with ESG and Sustainability Goals
Modern manufacturers must also meet ethical and environmental standards, an area where Mexico shines.
- Labor transparency: Enforceable labor laws under USMCA, with no forced labor concerns.
- Lower emissions: Shorter transport distances reduce carbon footprint by 20–40%.
- Green compliance: Facilities are more easily aligned with Western environmental and governance expectations.
Producing in Mexico helps companies protect their brand reputation and meet ESG goals more easily than in China.
10. Rising Nationalism and the “Friendshoring” Trend
In an age of shifting alliances, values now matter in supply chain planning.
- Friendshoring momentum: U.S. policy now favors investment in aligned countries, Mexico included.
- Local incentives: Laws like the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act promote North American sourcing, especially in automotive and clean energy.
- Positive perception: “Made in Mexico” is seen as more trustworthy by Western consumers and regulators.
Strategic alignment with the U.S. makes Mexico the default destination for future-facing, values-aligned supply chains.
Who Should Consider Manufacturing in Mexico?
While Mexico offers benefits for a wide range of industries, it’s particularly attractive for:
| Industry | Why It Works in Mexico |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Strong cluster in Bajio, skilled workforce, proximity to U.S. |
| Electronics & Tech | Guadalajara is called the "Silicon Valley of Mexico" |
| Furniture & Home Goods | Large capacity, skilled labor, access to raw materials |
| Textiles & Apparel | Lower tariffs, fast fashion-ready lead times |
| Aerospace | Growing hub with certified facilities and global clients |
Before engaging with any manufacturing partner, it’s essential to align on communication, quality standards, and timelines. This guide on How to Set Expectations with New Overseas Suppliers outlines the key steps to do it right from the start.
Potential Challenges to Consider
While Mexico presents a highly attractive case for nearshoring and manufacturing investment, it's important for businesses to assess potential risks and operational challenges before making the move. Below are key factors to keep in mind:
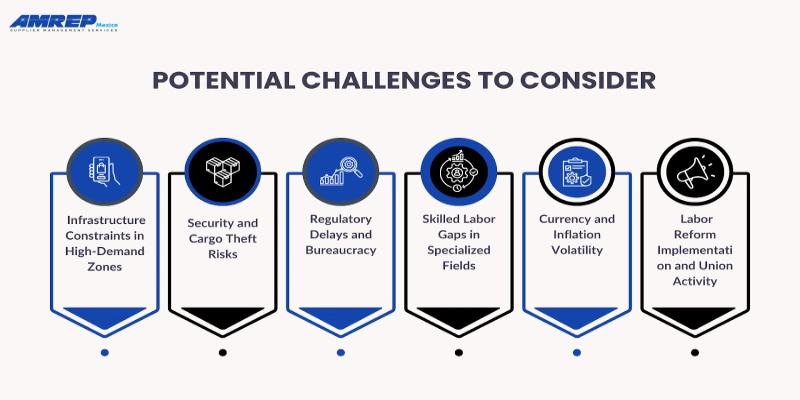
1. Infrastructure Constraints in High-Demand Zones
The nearshoring boom has significantly increased demand for industrial space and utilities, especially in popular manufacturing regions like Nuevo León, Baja California, and Jalisco.
- Vacancy rates in industrial parks are often below 3%, creating tight competition for space.
- Utilities such as electricity and water are strained in some locations due to rapid industrial growth.
- Skilled labor availability is tightening in certain technical fields as demand outpaces supply.
Businesses eyeing these zones should plan early, explore secondary cities, and engage with local stakeholders to secure infrastructure and workforce support.
2. Security and Cargo Theft Risks
While many industrial zones are well-protected, certain regions in Mexico continue to grapple with organized crime and logistics-related theft.
- Cargo theft remains a concern on some trucking routes, especially near major border crossings.
- Additional security costs such as guards, insurance, and route planning can affect bottom-line savings.
- Corruption at local levels may add friction during permitting or customs procedures.
Working with vetted logistics providers, implementing GPS tracking, and ensuring C-TPAT certification can significantly reduce exposure to these risks.
3. Regulatory Delays and Bureaucracy
Despite national efforts to streamline investment procedures, companies may still face bureaucratic slowdowns, especially at the local and municipal levels.
- Construction and environmental permits can take longer than expected.
- Import/export processes, though improved under USMCA, may still involve manual paperwork in some regions.
- Zoning approvals and utility hook-ups vary widely by state and may cause delays.
Collaborating with local consultants and legal advisors helps navigate this terrain efficiently and avoid hidden administrative hurdles.
4. Skilled Labor Gaps in Specialized Fields
Mexico boasts a large and growing technical workforce, but some skill sets remain in short supply, especially as more industries move operations there simultaneously.
- High demand in automation, robotics, clean tech, and advanced electronics has outpaced available talent in some regions.
- STEM education is strong, but experience in cutting-edge manufacturing can be limited outside of established clusters.
To overcome this, companies are investing in in-house training, partnerships with technical universities, and attractive benefit programs to retain skilled workers.
5. Currency and Inflation Volatility
While the Mexican peso has shown more stability in recent years, it remains susceptible to global market shocks.
- Fluctuations in exchange rates can affect supplier costs, payroll, and operating budgets.
- Post-pandemic inflation has increased prices for industrial land, utilities, and services in some regions.
Many companies mitigate this by structuring contracts in U.S. dollars or hedging against currency swings through financial planning.
6. Labor Reform Implementation and Union Activity
Mexico has made significant strides in aligning its labor laws with USMCA standards, aiming to protect workers' rights and democratize union representation.
- While positive overall, these changes can lead to initial instability as unions reorganize and assert new rights.
- Labor disputes and strikes, though not widespread, are possible during transitions.
- Employers may face stricter scrutiny over hiring practices, wages, and working conditions.
Proactive compliance, transparent HR policies, and regular audits can help companies stay ahead of evolving labor expectations.
In many ways, these challenges are simply the growing pains of a country ascending rapidly in global manufacturing relevance. The key to navigating them lies in choosing the right partners and locations. These decisions can make all the difference between setbacks and success.
That’s why it’s essential to thoroughly vet your manufacturing partner before committing. Our Sourcing Checklist: 10 Things to Check Before Signing with a Manufacturer outlines the most critical areas to review, helping you minimize risk and start off on the right foot.
Is Mexico Right for You?
The shift from China to Mexico isn't just a trend; it’s a strategic evolution of global manufacturing. The evidence is clear: Mexico has emerged as a highly attractive destination for manufacturing investment, especially when targeting the U.S. market. It offers a rare combination of cost efficiency, quality production, and strategic advantages that China, in today’s environment, cannot provide to U.S. companies.
At AMREP Mexico, we specialize in helping companies transition seamlessly into Mexico’s thriving manufacturing ecosystem. From Supplier Audits and quality assurance to comprehensive sourcing solutions and vendor management, our team ensures your operations meet the highest standards from day one. With decades of experience, we make it easier to operate with confidence, speed, and efficiency.


